多线程
进程与线程区别: 进程需要分配独立的内存空间;线程在同一内存空间中工作,可以共享同一块内存和系统资源
与Java相关的API:
1)Thread类
方法:start()启动; urn() ; getName()获取线名; setName()改变线名; setPriority()设置优先级; setDaemon()守护线程; join()等待; interupt()中段本线程;
isAlive()判断运行是否仍在生命周期之中; yield()静态,停止线程运行;
2)Runnable类(公共规范)
3)Object类
方法:wait()等待; notify()唤醒线程; notifyAll()唤醒所有线程
线程的创建:
1)继承Thread类
步骤:A、创建一个继承Thread类的类
B、在子类中重写run()方法,写自己想要运行的代码
C、创建Thread类的实例
D、调用实例上的start()方法,开始运行线程
2)实现Runnable接口
步骤:A、创建一个类实现Runnable接口
B、在Runnable指定的run()方法内,写自己想要运行的代码
C、创建Runnable类的实例
D、创建一个Thread对象,将Runnable的实例作为构造器参数传进去
E、调用Thread类的实例的start()方法
线程优先级介于:1——10之间;线程运行顺序是由优先级决定;setPriority()设置线程优先级,getPriority()取得线程优先级
线程同步(互斥):
作用:给所在对象加锁(监视器),就是当这个线程启动时别的线程无法使用
同步块格式:Synchronized(取得锁的对象){//要锁定的代码}
死锁:释放之后都无法运行,需要考虑优先顺序释放的
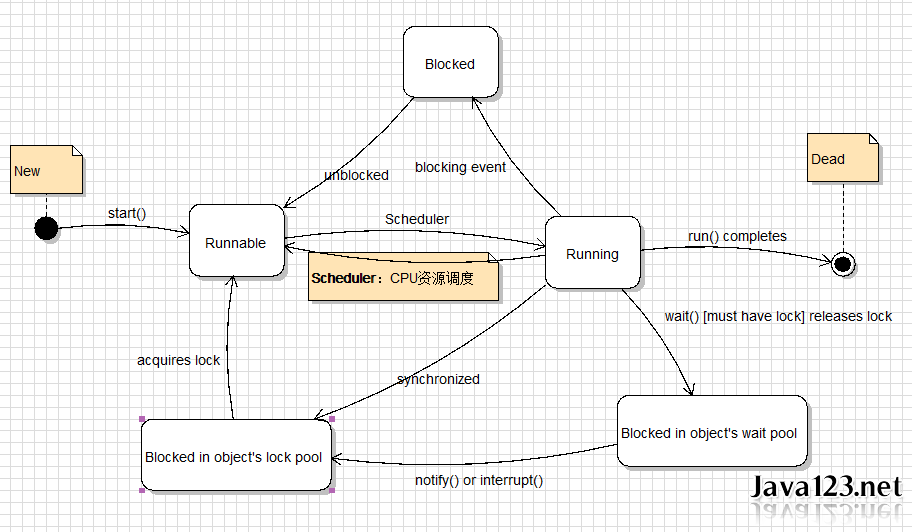
线程的生命周期:
Java的线程会因为实例化而产生,也可能因为run()程序运行完成后而结束,线程在运行的过程之中也可能会休眠(sleep),让出(yield),也可能必须等待其他的线程
处于Runnable状态的线程会因为优先权的不同,而又JVM决定该进入Runing状态,同时的线程也会因为自行调用yield()方法而重新回到Runnable状态。处于Runing状态也会因调用了sleep()方法
而进入阻塞(blocked)的状态,一直等到线程的休眠结束后而重新回到Runnable的状态,处于Rining状态的线程也可能因为再启动其他的线程,但却由于另一个线程调用了join()方法而必须进入阻塞
的状态,原线程会一直等到所启动的线程运行完毕后,原线程才会再进入Runnable状态,并等待取得运行权
修正线程的状态图:
第一次:线程有可能因为无法取得某个对象的对象锁而无法处于Runing的状态,此程让线程会由 Runing的状态被丢到该对象的锁池中并等待取得该对象锁,如果该对象锁已经被释放了,则在锁池中的某个线程会进入Runnable状态等待运行,如果取得对象锁的线程在等待运行的期间对象锁又被另一个线程取得,则原来的线程又会无法运行
第二次:
Java I/O系统
I:是Input为输入; O:是output为输出
流(是 I/O的抽象和基础)
分类:1)按方向分:
输入流:从数据源读取数据到程序
输出流:将数据从程序写入数据的目的地
2)按单位分:
字节流:内存变量类型为byte()
1 package com.lovo; 2 3 import java.io.File; 4 import java.io.FileInputStream; 5 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 6 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 7 import java.io.IOException; 8 import java.io.InputStream; 9 import java.io.OutputStream;10 11 /**12 * 字节输入输出流测试13 * 14 * @author 小明15 *16 */17 public class IOTest {18 19 public static void main(String[] args) {20 StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer(); // 字符串缓冲21 22 /* 输入流 */23 InputStream in = null;24 25 try {26 // 1. 打开输入流27 in = new FileInputStream("E:\\jg\\exercise.txt");28 // 2. 读取29 // byte[] b = new byte[128];30 byte[] b = new byte[1024 * 4];31 int len = in.read(b); // 返回读取到的字节数,返回-1表示读取到流结尾32 while(len != -1){33 buffer.append(new String(b, 0, len)); // 将读取到的字节解析为String追加到缓冲34 len = in.read(b);35 }36 // System.out.println("读到" + len + "字节的数据");37 System.out.println(buffer.toString());38 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {39 e.printStackTrace();40 } catch (IOException e) {41 e.printStackTrace();42 } finally {43 // 3. 释放资源,关闭输入流44 if (in != null){45 try {46 in.close();47 } catch (IOException e) {48 e.printStackTrace();49 }50 }51 }52 53 /* 输出流 */54 OutputStream out = null;55 56 try {57 File file = new File("D:\\test\\demo\\test.txt");58 if (!file.getParentFile().exists()){ // 文件路径不存在,则创建路径中所有不存在的目录59 file.getParentFile().mkdirs();60 }61 // 1. 打开输出流62 out = new FileOutputStream(file);63 // 2. 写64 out.write(buffer.toString().getBytes());65 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {66 e.printStackTrace();67 } catch (IOException e) {68 e.printStackTrace();69 } finally {70 // 3. 释放输出流资源71 if (out != null){72 try {73 out.flush();74 out.close();75 } catch (IOException e) {76 e.printStackTrace();77 }78 }79 }80 }81 } 字符流:内存变量类型是char();
1 package com.lovo; 2 3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 4 import java.io.FileReader; 5 import java.io.FileWriter; 6 import java.io.IOException; 7 import java.io.Reader; 8 import java.io.Writer; 9 10 /**11 * 字符输入输出流测试12 * 13 * @author 小明14 *15 */16 public class IOTest2 {17 18 public static void main(String[] args) {19 StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();20 21 /* 输入流 */22 Reader reader = null;23 24 try {25 // 1. 打开流26 reader = new FileReader("E:\\jg\\exercise.txt");27 // 2. 读取28 char[] ch = new char[128]; // 缓冲区29 int len;30 do {31 len = reader.read(ch);32 if (len == -1)33 break;34 buffer.append(new String(ch, 0, len));35 } while (len != -1);36 System.out.println(buffer.toString());37 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {38 e.printStackTrace();39 } catch (IOException e) {40 e.printStackTrace();41 } finally {42 // 3. 释放资源43 if (reader != null) {44 try {45 reader.close();46 } catch (IOException e) {47 e.printStackTrace();48 }49 }50 }51 52 /* 输出流 */53 54 Writer writer = null;55 56 try {57 // 1. 打开流58 writer = new FileWriter("d:\\test.txt");59 // 2. 写入60 writer.write(buffer.toString());61 } catch (IOException e) {62 e.printStackTrace();63 } finally {64 // 3. 释放资源65 if (writer != null) {66 try {67 writer.flush();68 writer.close();69 } catch (IOException e) {70 e.printStackTrace();71 }72 }73 }74 }75 }
文件类:
File类:提供了管理磁盘文件和目录的基本功能,File对象代表一个文件或目录的名称和位置的字符串
1 package com.lovo; 2 3 import java.io.File; 4 import java.io.FileInputStream; 5 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 6 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 7 import java.io.IOException; 8 import java.io.InputStream; 9 import java.io.OutputStream;10 11 /**12 * 字节输入输出流测试13 * 14 * @author 小明15 *16 */17 public class IOTest {18 19 public static void main(String[] args) {20 StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer(); // 字符串缓冲21 22 /* 输入流 */23 InputStream in = null;24 25 try {26 // 1. 打开输入流27 in = new FileInputStream("E:\\jg\\exercise.txt");28 // 2. 读取29 // byte[] b = new byte[128];30 byte[] b = new byte[1024 * 4];31 int len = in.read(b); // 返回读取到的字节数,返回-1表示读取到流结尾32 while(len != -1){33 buffer.append(new String(b, 0, len)); // 将读取到的字节解析为String追加到缓冲34 len = in.read(b);35 }36 // System.out.println("读到" + len + "字节的数据");37 System.out.println(buffer.toString());38 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {39 e.printStackTrace();40 } catch (IOException e) {41 e.printStackTrace();42 } finally {43 // 3. 释放资源,关闭输入流44 if (in != null){45 try {46 in.close();47 } catch (IOException e) {48 e.printStackTrace();49 }50 }51 }52 53 /* 输出流 */54 OutputStream out = null;55 56 try {57 File file = new File("D:\\test\\demo\\test.txt");58 if (!file.getParentFile().exists()){ // 文件路径不存在,则创建路径中所有不存在的目录59 file.getParentFile().mkdirs();60 }61 // 1. 打开输出流62 out = new FileOutputStream(file);63 // 2. 写64 out.write(buffer.toString().getBytes());65 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {66 e.printStackTrace();67 } catch (IOException e) {68 e.printStackTrace();69 } finally {70 // 3. 释放输出流资源71 if (out != null){72 try {73 out.flush();74 out.close();75 } catch (IOException e) {76 e.printStackTrace();77 }78 }79 }80 }81 }
高级字节流分类:
1)过滤流:(都是FileInputStream和FileOutputStream的子类)
分类:缓冲流:BufferedFileInputStream和BufferedOutputStream
数据流:DateInputStream和DateOutputStream
计数:LineNumberInputStream(表明正在读取哪一行)
推回数据流:PushbackInputStream
打印数据流:PrintStream(带刷新功能)
2)对象流:ObjectInputStream和ObjectOutputStream
3)合并:sequenceInputStream
高级字符流:
1)缓冲流:BufferedReader和BufferedWriter
2)转换流:InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter(字节-字符)
3)打印输出流:PrintWriter
对象流:
序列化:ObjectInputStream(保存内存中对象的“全景图”)为了实现对象序列化,对应的类必须实现java.io.Serializable接口
反序列化:ObjectOutputStream
属性加上一个transient修饰符,其职不被序列化
Java图形用户界面编程
AWT:抽象窗口工具箱,保证平台独立性,但严重依赖下层操作系统——重量组件
Swing:具有更好的平台无关性和可移植性——轻量组件。
组件三要素:(内容)、(外观显示)、(行为)
组件三个部分:模型 、视图、控制器
认识几个方法
add( ):将组件添加到该容器中。
removeAll() :移掉容器中的全部组件。
remove(Component c) 移掉容器中参数指定的组件。
validate():每当容器添加新的组件或移掉组件时,调用该方法以保证容器中的组件能正确显示出来。
重量级容器:JFram(窗体)、JDialog(对话框)、JWindow(窗口)、JApplet(小程序),继承自Container容器类
Swing菜单:
1 /** 2 * 添加菜单 3 */ 4 public void addMenu() { 5 // 菜单条 6 JMenuBar jMenuBar = new JMenuBar(); 7 // 将菜单条加入到当前窗体 8 this.setJMenuBar(jMenuBar); 9 10 // 菜单11 JMenu file = new JMenu("文件");12 jMenuBar.add(file);13 14 // 子菜单15 JMenu newFile = new JMenu("新建");16 newFile.add("Java项目");17 newFile.add(".Net项目");18 file.add(newFile);19 20 // 子菜单项21 JMenuItem open = new JMenuItem("打开...");22 file.add(open);23 file.add("保存");24 file.add("另存为");25 26 // 获取“保存”菜单项27 JMenuItem save = file.getItem(2);28 save.setEnabled(false); // 禁用29 30 // 为"打开"菜单项添加快捷键31 open.setAccelerator(KeyStroke.getKeyStroke(KeyEvent.VK_O,32 InputEvent.CTRL_MASK));33 } 布局:
1)流式布局管理器:FlowLayout
2)边框布局管理器:BorderLayout
3)网格布局管理器:Griflayout(可传递两个或四个或无参数)
4)盒式布局管理器:Boxlayout
1 /** 2 * 添加按钮 3 */ 4 public void addButton() { 5 6 // 单行文本框 7 JTextField text = new JTextField("请输入文本"); 8 this.add(text, BorderLayout.NORTH); 9 10 /* 默认边界布局管理器 */11 // 按钮12 JButton west = new JButton("West");13 JButton east = new JButton("East");14 JButton north = new JButton("North");15 JButton south = new JButton("South");16 JButton center = new JButton("Center");17 // // 添加按钮18 // this.add(west, BorderLayout.WEST);19 // this.add(east, BorderLayout.EAST);20 // this.add(north, BorderLayout.NORTH);21 // this.add(south, BorderLayout.SOUTH);22 // this.getContentPane().add(center, BorderLayout.CENTER);23 24 // 创建面板对象25 JPanel pnl = new JPanel();26 27 /* 网格布局管理器 */28 GridLayout layout = new GridLayout(3, 2, 10, 10);29 // this.setLayout(layout);30 31 // this.add(west);32 // this.add(east);33 // this.add(north);34 // this.add(south);35 // this.add(center);36 37 pnl.setLayout(layout);38 pnl.add(west);39 pnl.add(east);40 pnl.add(north);41 pnl.add(south);42 pnl.add(center);43 44 this.add(pnl, BorderLayout.CENTER); 文本框和口令框:
JTextField t=new JTextField() ;
JPassworField j=new JPassworField ();
布局管理让容器使用方法setLayout(布局对象)来设计自己的布局
事件和事件源:
点击按钮:JButton 文本框中按回车键:JTexFiled 选中一个新条目:JComboBox 选中条目:JList 点击检查框:JCeckBox
点击单选按钮:JRadioButton 选中菜单栏:JMenuTtem 移动滚动条:JScroIIBar、JSlider 关于窗口动作:Window
鼠标动作:Component 移动或拖拽:Component 键按下或释放:Component 组件添加或删除:Container 组件移动、恢复、隐藏、显示:Component
事件监听器、注册和处理事件:
使用事件委托模型来处理事件,事件源触发一个事件,但是事件源本身并不处理该事件,而是委托给该事件有兴趣的对象来处理,其对象称为事件监听器
需做:1)创建一个监听器对象,必须对应事件监听器的接口实例(某个类型的事件XxxEvent,对应接口为XxxListener)
2)将监听器对象注册到事件源上(对于XxxEvet注册为addXxxListener)
定义监听器类:
1)将监听器定义在单独的类中
2)让CUI程序本身实现监听器接口
3)使用内部类定义监听器
4)使用匿名内部类定义监听器。